What is virtual memory?
My favorite definition, provided by memorydepot.com:
This is system memory that is simulated by the hard drive. When all the RAM is being used (for example if there are many programs open at the same time) the computer will swap data to the hard drive and back to give the impression that there is slightly more memory.
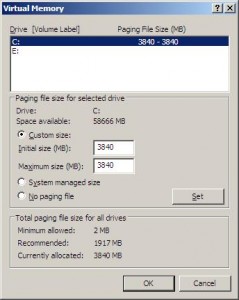
How do I access the Virtual Memory Setting?
- Right click “computer” in the start menu, or “my computer” on the desktop
- Left click “Properties”
- Select the “Advanced” tab on the Properties Dialogue
- Select “Settings” under the “Performance” section of the screen
How do I optimize my virtual memory?
Provided you have hard drive space available to accommodate, you have two goals when you are setting your virtual memory:
- You want your full memory to be able to “dump” completely into the available hard drive space. This is why Microsoft recommends that your initial settings = 1.5 times the amount of available physical memory, and this figure is generally what is displayed in the “recommended” setting.
- Your second objective however, is to prevent unnecessary fragmentation on your hard drive. Microsoft’s recommended maximum setting = 3 times the available physical memory. However, by allowing such a setting that the virtual paging file is essentially growing a shrinking over time, excessive fragmentation is created on the hard drive (1’s and 0’s getting jumbled up, slowing down your machine over time.) By setting both your minimum and your maximum to 3 times the available physical memory, you have achieved both objectives.
This is system memory that is simulated by the hard drive. When all the RAM is being used (for example if there are many programs open at the same time) the computer will swap data to the hard drive and back to give the impression that there is slightly more memory.